Relational Model:
The Relational Model represents how data is stored in Relational Databases. The Relational Model uses Collection of tables to represent data and relationship among them.
Features:
- Data is organized in terms of rows & columns in a table.
- The intersection of a row and column must give a simple value.
- Does not maintain Physical Connection.
Implementation:
- The Relational Model is implemented with the help of two- dimensional array.
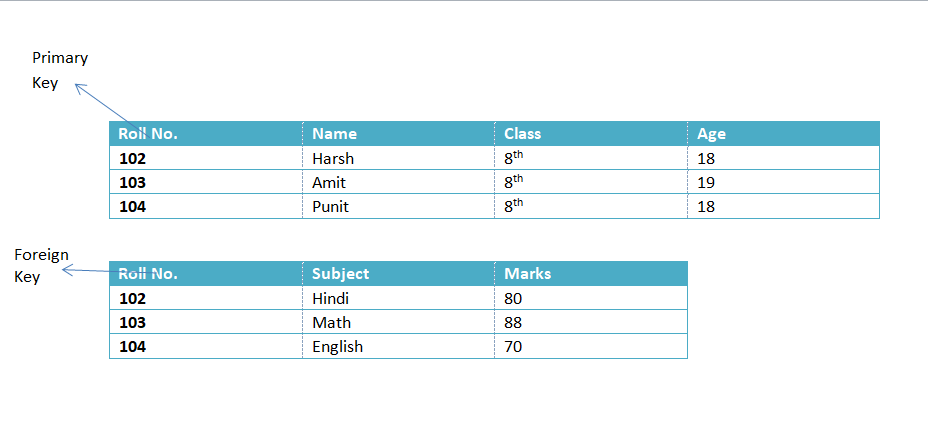
- The field which is common in all data files and is used to link all of them as a database is called Key Field.
- For Example: In table, we see that Roll No. is common in both table is called key field as well as foreign key.
Key Characteristics of Relational Model:
-
Tables (Relations): Data is organized into tables, also known as relations. Each table consists of rows (tuples) and columns (attributes). The rows represent individual records, and the columns represent attributes or fields.
-
Columns (Attributes): Each column in a table represents a specific attribute or characteristic of the data. Columns have names, data types, and constraints that define the kind of data they can store.
-
Rows (Tuples): Rows in a table represent individual records or instances of data. Each row contains a set of values, one for each attribute/column in the table.
-
Primary Key: Each table has a primary key, which is a unique identifier for each row in the table. The primary key ensures the uniqueness of each record and is used to establish relationships between tables.
-
Foreign Key: Foreign keys are used to establish relationships between tables. A foreign key in one table refers to the primary key in another table, creating a link between the two tables.
-
Data Integrity: The relational model enforces data integrity through constraints such as primary key constraints, foreign key constraints, and data type constraints. This ensures the accuracy and consistency of the data.
-
Normalization: Normalization is a process used to organize data in a way that reduces redundancy and dependency. It involves breaking down tables into smaller, more manageable pieces to minimize data duplication.
-
Structured Query Language (SQL): SQL is the standard language for interacting with relational databases. It provides a set of commands for creating, querying, updating, and deleting data in a relational database.
Advantages of Relational Model:
-
Data Integrity: The relational model enforces data integrity through constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, and unique constraints. This ensures that data is accurate and consistent.
-
Flexibility: It allows for flexible querying using the Structured Query Language (SQL). Users can easily retrieve and manipulate data without having to know the underlying physical storage details.
-
Normalization: The relational model supports normalization techniques, which help reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. This is achieved by organizing data into well-structured tables.
- Scalability: Relational databases can handle large amounts of data and scale well as the volume of data increases. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications from small-scale to enterprise-level systems.
-
Complex Queries: The relational model supports complex queries involving multiple tables through the use of JOIN operations. This allows users to retrieve information from multiple tables in a single query.
-
Security: Relational databases offer features such as access control and user authentication, enhancing data security by restricting unauthorized access to sensitive information.
-
Standardization: The relational model is well-defined and has become a standard in the industry. This standardization promotes interoperability and allows for the development of various tools and applications that work with relational databases.
Disadvantages of Relational Model:
-
Performance: In certain scenarios, the relational model may not perform as well as other data models, especially when dealing with complex queries or large datasets. Optimizing performance may require experienced database administrators.
-
Scalability Challenges: While relational databases can scale, there may be challenges in scaling horizontally across multiple servers, especially in distributed environments. NoSQL databases may offer better scalability in some cases.
-
Fixed Schema: The relational model relies on a fixed schema, meaning that changes to the structure of the database (adding or removing columns) can be challenging and may require downtime.
-
Complexity for Simple Data: For simple and straightforward data storage and retrieval needs, a relational database may introduce unnecessary complexity. In such cases, a NoSQL database might be a more suitable alternative.
