PGP Encryption:
PGP stands for “Pretty Good Privacy.” It’s a data encryption and decryption program used for secure communication and data protection. Developed by Phil Zimmermann in 1991, PGP provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication, including emails, files, and text messages.
Working of PGP:
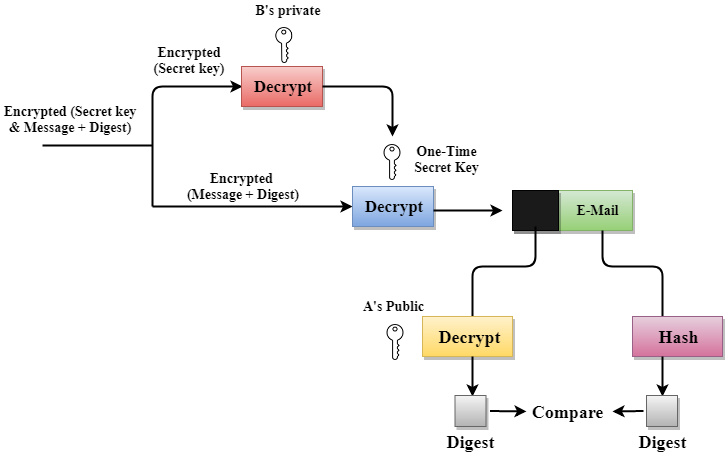
PGP, or Pretty Good Privacy, facilitates secure communication and data protection through a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques. Users generate a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. When sending a message, the sender encrypts it using the recipient’s public key, ensuring only the recipient can decrypt it using their private key. PGP also supports digital signatures, allowing senders to sign messages with their private keys, providing authentication and integrity verification for the recipient. Recipients verify signatures using the sender’s public key. PGP’s comprehensive approach to encryption and authentication ensures confidentiality, authenticity, and integrity in communication.
Where Can You Use PGP?
- Email Encryption: PGP can encrypt email messages and attachments, ensuring that only the intended recipient can read the contents.
- File Encryption: PGP can encrypt files and folders stored on a computer or transferred over networks, safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Secure Messaging: PGP can be used for secure messaging platforms, allowing users to exchange encrypted messages and files securely.
- Digital Signatures: PGP can generate and verify digital signatures, providing authentication and integrity verification for documents, contracts, and software distributions.
- Secure File Transfer: PGP can secure file transfers over the internet or other networks, protecting data in transit from interception or tampering.
