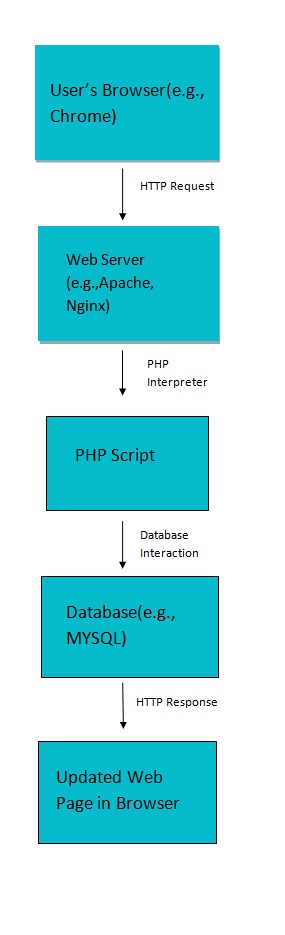
Explanation:
- User’s Browser: This is where a user interacts with a website.
- Web Server: The user’s request is first handled by a web server (e.g.,Apache or Niginx). The server may serve static content directly, but for dynamic content or PHP scripts, it passes the request to the PHP interpreter.
- PHP Interpreter: The PHP interpreter processes the PHP script, executes the code, and may interact with a database or other resources.
- PHP Script: The PHP script contains the logic for generating dynamic content or performing actions on the server. It may be including HTML, PHP code, and other assets.
- Database Interaction: PHP scripts often interact with databases (e.g.,MySQL) to retrieve or store data.
- HTTP Response: The final result, generated by the PHP script, is sent back to the web server, which then delivers it as an HTTP response to the user’s browser.
- Updated Web Page in Browser: The user’s browser receives the HTTP response and updates the web page accordingly.
This is a simplified overview, and in a real-world scenario, there might be additional components and interactions, such as caching, security measures, and external services.
