Text Alignment (text-align):
Definition:
The text-align property in CSS is used to set the horizontal alignment of text content within a block-level element or table cell. It specifies whether the text should be aligned to the left, right, center, or justified within its containing element.
Syntax:
HTMLselector { text-align: value; }
selector: The HTML element or class to which the styling is applied.value: The alignment value, which can be one of the following:left,right,center, orjustify.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.center-text {
text-align: center;
}
.right-text {
text-align: right;
}
.justified-text {
text-align: justify;
}
</style>
<title>Text Alignment Example</title>
</head>
<body>
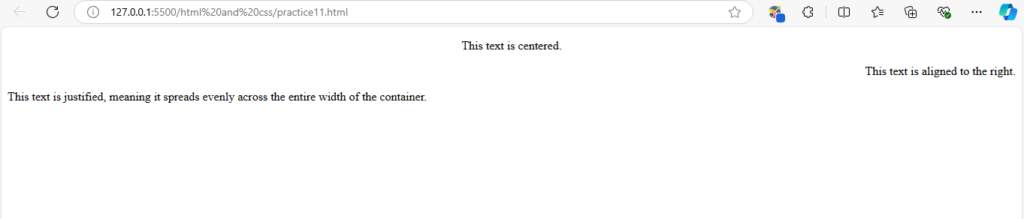
<div class="center-text">
<p>This text is centered.</p>
</div>
<div class="right-text">
<p>This text is aligned to the right.</p>
</div>
<div class="justified-text">
<p>This text is justified, meaning it spreads evenly across the entire width of the container.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
output:
Explanation:
A. HTML Structure:
- Create a basic HTML file with three
divelements, each having a different class (center-text,right-text,justified-text).
B. CSS Styles:
- Use the
text-alignproperty to set the horizontal alignment of the text within eachdiv.
.center-text: Text is centered..right-text: Text is aligned to the right..justified-text: Text is justified, spreading evenly across the container.
