Number System
The number system is a way to represent numbers using a set of digits or symbols. There are several types of number systems, but three of the most commonly used ones are binary, octal, and decimal. Let’s take a look at each system with examples:
1. Binary Number System (Base 2)
In the binary number system, there are only two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit in a binary number represents a power of 2.
- Base: 2
- Digits:
0, 1
Octal Number System (Base 8)
The octal number system is a base-8 number system, meaning it uses 8 digits:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
In the octal system, each place value is a power of 8, similar to how the decimal system uses powers of 10. For example:
- The rightmost digit represents 80 (ones place),
- The next digit represents 81 (eights place),
- The next digit represents 82 (sixty-four place),
- And so on.
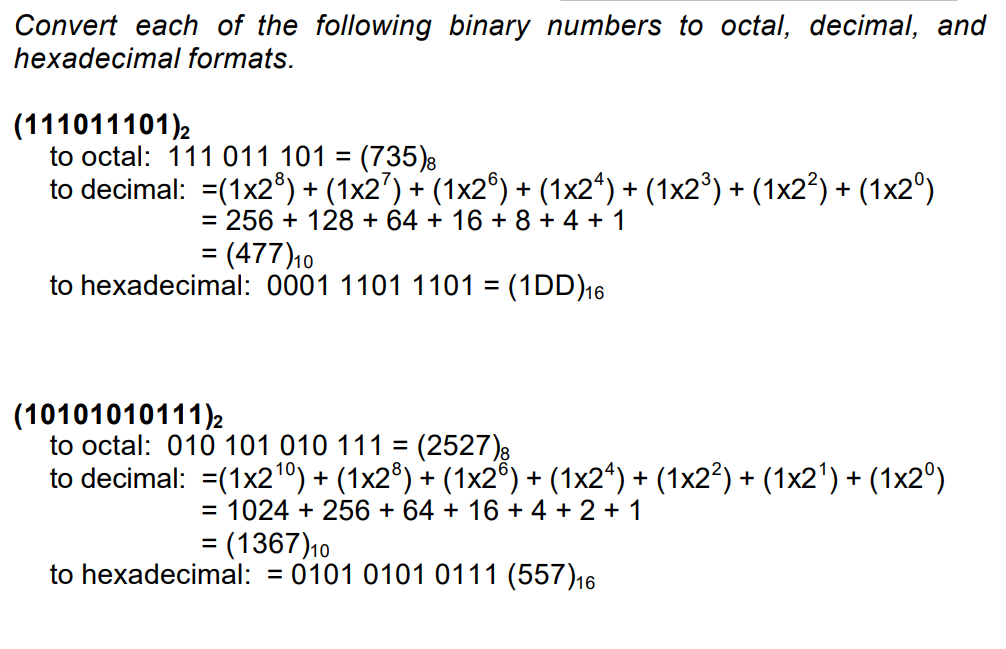
Convert each of the following octal numbers to binary, decimal, and
hexadecimal formats.

Decimal Number System (Base 10)
The decimal number system is the number system most commonly used in everyday life. It is a base-10 system, meaning it uses 10 digits:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
In the decimal system, each digit’s place represents a power of 10. For example:
- The rightmost digit represents 100 (ones place),
- The next digit represents 101 (tens place),
- The next digit represents 102 (hundreds place), and so on.
Convert each of the following decimal numbers to binary, octal, and
hexadecimal formats.

Hexadecimal Number System (Base 16)
The hexadecimal number system is a base-16 system, meaning it uses 16 digits:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F.
- The digits 0 to 9 represent their usual values (0, 1, 2, …, 9).
- The digits A to F represent the decimal values 10 to 15:
- A = 10
- B = 11
- C = 12
- D = 13
- E = 14
- F = 15
In the hexadecimal system, each place value is a power of 16. For example:
- The rightmost digit represents 160 (ones place),
- The next digit represents 161 (sixteens place),
- The next digit represents 162 (two hundred fifty-sixes place),
- And so on.
Convert each of the following hexadecimal numbers to binary, octal, and
decimal formats.

