Data Types:
In C programming, data types are used to define the type of data that a variable can store. C provides a variety of data types that can be broadly categorized into two main groups: primary (or built-in) data types and derived data types.
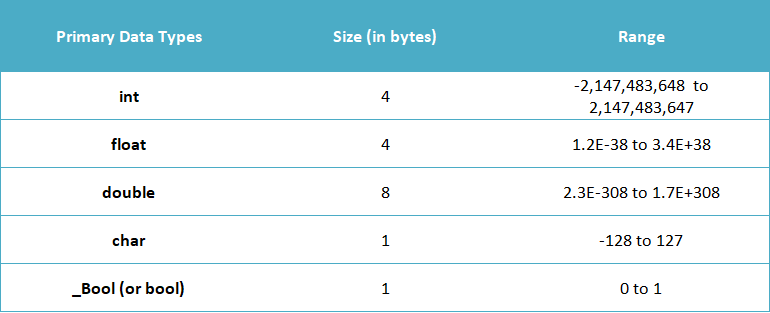
1.Primary (Built-in) Data Types:
These are the fundamental data types provided by the C language, and they directly represent the basic building blocks for data manipulation.
Explanation:
- int: Represents integer values.
Syntax: int variableName;
Example: int age;
- float: Represents floating-point numbers (real numbers).
Syntax: float variableName;
Example: float temperature;
- _Bool (or bool): Represents boolean values (true or false).
Syntax: _Bool variableName; or bool variableName; (after including <stdbool.h>).
Example: _Bool isTrue;
// or
bool isValid;
- char: Represents single characters.
Syntax: char variableName;
Example: char grade;
- double: Represents double-precision floating-point numbers.
Syntax: double price;
Example: _Bool isTrue;
// or
bool isValid;
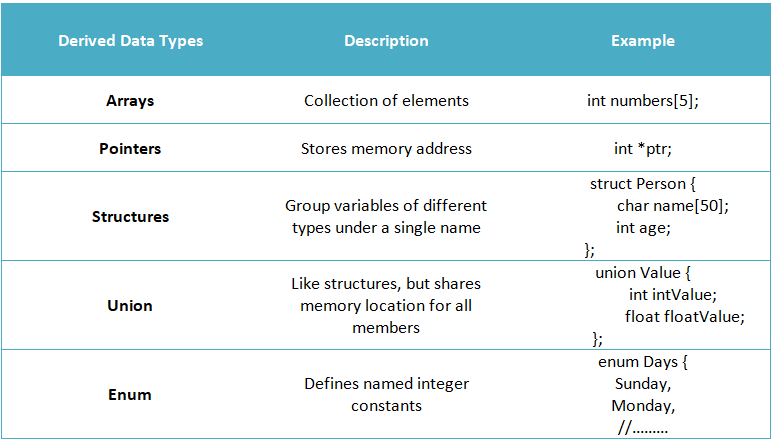
2.Derived (Built-in) Data Types:
Derived data types are created by combining primary data types. They include structures, unions, arrays, pointers, and enumerations.
Explanation:
- Arrays: Represents a collection of elements of the same data type.
Syntax: dataType arrayName[size];
Example: int numbers[5];
- Pointers: Stores the memory address of another variable.
Syntax: dataType *pointerName;
Example: int *ptr;
- Structures: Allows grouping variables of different data types under a single name.
Syntax: struct structureName {
dataType member1;
dataType member2;
// …
};Example: struct Person {
char name[50];
int age;
};
- Union: Similar to structures but shares the same memory location for all its members.
Syntax: union unionName {
dataType member1;
dataType member2;
// …
};Example: union Value {
int intValue;
float floatValue;
};
- Enum: Defines a set of named integer constants.
Syntax: enum enumName {
constant1,
constant2,
// …
};Example: enum Days {
Sunday,
Monday,
// …
};