Conditional statements in C are used to make decisions in a program based on the evaluation of a condition. These statements allow the program to execute different blocks of code depending on whether a specified condition is true or false. The primary conditional statements in C are the if, else if, and else statements.
1. if Statement:
‘if‘ Statement is used in conditional expressions. It is used when a set of statements are executed depending upon a specified condition. The condition is specified using ‘if’ statement. If Condition is true, then a set of statements is executed otherwise statements written after statements of ‘if’ condition is executed.
Flow-Chart:
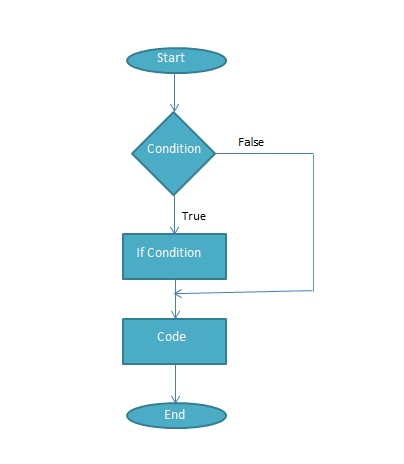
Syntax:
if (condition) {
// Code to be executed if the condition is true
}
Example: Program to find no. is even or odd.
#include <stdio.h>int main(){// Declare a variable to store the user’s inputint number;// Prompt the user to enter a numberprintf(“Enter an integer: “);scanf(“%d”, &number);// Check if the number is even or odd using the modulo operatorif (number % 2 == 0){// If the remainder is 0, the number is evenprintf(“%d is an even number.n”, number);}return 0;}
Output:
Enter an integer: 2
2 is an even number.
2. if-else Statement:
This Statement is used if there are two possible results of a question. If statement is true, then statements written in ‘if ‘clause will be executed otherwise statements written in ‘else’ clause will be executed.
Flow-Chart:
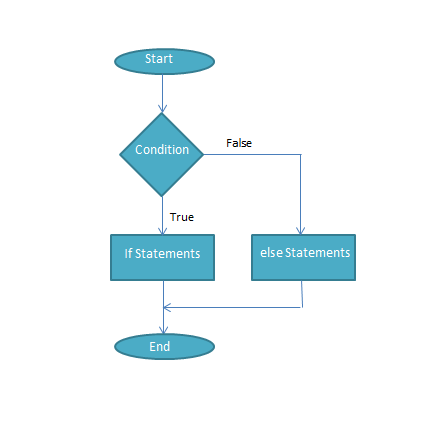
Syntax:
if (condition) {
// Code to be executed if the condition is true
} else {
// Code to be executed if the condition is false
}
Example: Program to find a person is eligible for vote or not.
#include <stdio.h>int main(){// Declare a variable to store the ageint age;// Prompt the user to enter their ageprintf(“Enter your age: “);scanf(“%d”, &age);// Check if the person is eligible to voteif (age >= 18){printf(“Congratulations! You are eligible to vote.n”);}else{printf(“Sorry, you are not eligible to vote. You must be at least 18 years old.n”);}return 0;}
Output:
Enter your age: 19
Congratulations! You are eligible to vote.
3. else-if / nested if Statement:
A nested if in ‘C‘ is an ‘if’ statement that is the target of another ‘if’ statement. It means an if statement inside another ‘if’ statement.
Flow-Chart:
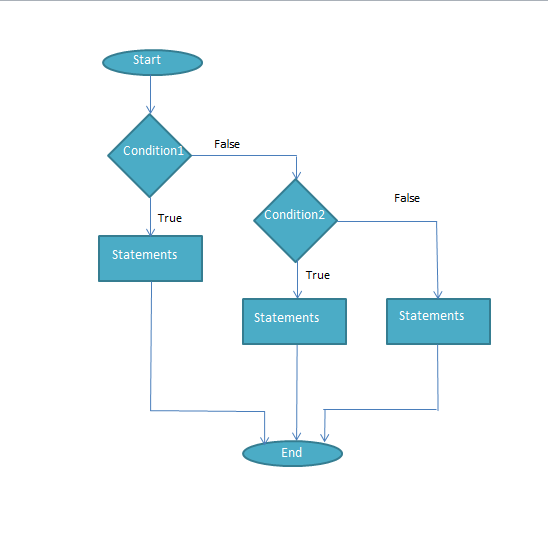
Syntax:
if (condition1) {
// Code to be executed if condition1 is true
}else
if (condition2) {
// Code to be executed if condition2 is true
}else {
// Code to be executed if none of the conditions are true
}
Example: Program to find greatest among three numbers.
#include <stdio.h>int main(){// Declare variablesint a,b,c;printf(“Enter the value of a, b, c: “);scanf(“%d %d %d”, &a, &b, &c);if ((a>b)&&(a>c)){printf(“a is greatest.n”);}elseif ((b>a)&&(b>c)){printf(“b is greatest.n”);}elseprintf(“c is greatest.n”);return 0;}
Output:
Enter the value of a, b, c: 77
65
78
c is greatest.
